E-Invoicing in Malaysia: All That You Need to Know
Until the early 2000s, paper invoices were the norm. And while they’d make transactions and record keeping straightforward, they’d also cause the process to be time-consuming, labour-intensive and prone to errors. The difficulty of tracking inconsistencies also meant that with the eventual boom of the technology, digitising the invoicing system became one of the initial priorities of countries around the world.
Notable reforms in e-invoicing began in Chile (2001), which first made electronic invoicing legal and later mandatory. Similarly, Mexico rolled out CFDI (Comprobante Fiscal Digital por Internet), in 2004 which improved the taxation efficiency by more than 30% in the first few years.
Compared to the rest of the world, Malaysia’s journey towards e-invoicing started late in 2023. However, since then, the government has been consistently and gradually carrying out implementation across several industries in phases. The digital invoicing system will be made mandatory for most Malaysian businesses by 2026.
This article provides comprehensive information on the concept and compliance requirements for e-invoicing in Malaysia.
What is E-Invoicing?
E-invoicing is the electronic generation, transmission, and storage of invoices. These invoices are structured and stored according to the guidelines provided by the governing authority of the respective country or state in which the business is. In Malaysia’s case, the Inland Revenue Board (IRBM) governs the e-invoices.
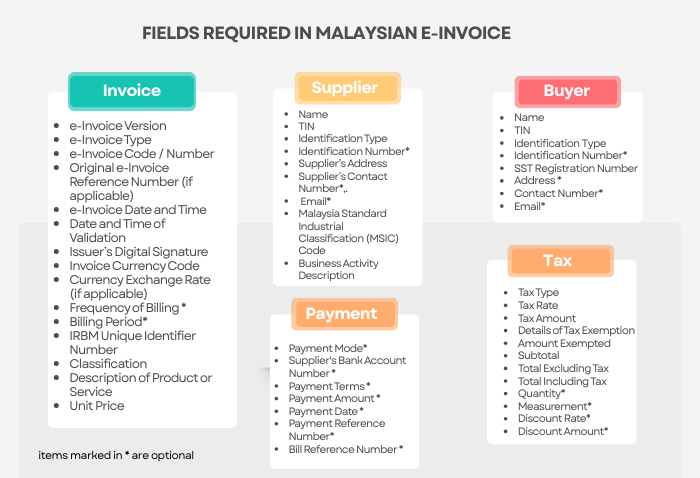
Based on the guidelines, each e-invoice in Malaysia must be stored in a UBL 2.1 format (XML or JSON) and must have 55 fields, out of which 37 are mandatory. Similarly, every invoice generated in Malaysia requires a Digital Certificate issued by IRBM.
Who is E-Invoicing Applicable to in Malaysia?
All taxpayers undertaking commercial activities in Malaysia (B2B, B2G, and B2C) are required to issue e-invoices. This includes:
- Corporations
- Limited liability partnerships
- Partnerships
- Sole proprietors
- Other legal entities
Are There Any Exemptions from E-invoicing?
Yes, there are. In general, businesses with less than RM 500,000 in revenue are exempted. And while we’ve given general information about the exemptions here, remember that these exemptions are mostly sector-specific, so you might need to refer to the official information from IRBM.
🏢 Small Businesses
Businesses with an annual turnover below RM500,000 are exempt from mandatory e-invoicing.
🏥 Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers are currently exempt from issuing e-invoices under Malaysia’s e-invoicing guidelines.
💰 Financial Services
Certain financial services including banking, insurance, and takaful have sector-specific exemptions; compliance depends on activity type.
🚀 New Businesses
New businesses with initial annual turnover below RM500,000 are exempt until they exceed the threshold in subsequent years.
🏛️ Government Agencies & Authorities
Exemptions include:
- Existing and Former Ruler and Ruling Chief (except former Governor or Yang di-Pertua Negara)
- Royal Consorts (Raja Perempuan, Sultanah, Tengku Ampuan, etc.)
- Government agencies, State & Local authorities
- Statutory bodies and statutory authorities, including facilities under these bodies
- Foreign diplomatic & consular offices
Specific Deadlines for Based on Company Type: E-Invoicing Implementation Timeline
The following is the e-invoicing implementation timeline according:
| Effective Date | Businesses Covered (Annual Turnover) |
|---|---|
| August 1, 2024 | Businesses with an annual turnover exceeding RM100 million |
| January 1, 2025 | Businesses with an annual turnover exceeding RM25 million |
| July 1, 2025 | Businesses with an annual turnover exceeding RM500,000 |
| January 1, 2026 | Businesses with an annual turnover exceeding RM150,000 |
| July 1, 2026 | Businesses with an annual turnover of up to RM1 million |
| December 31, 2026 | All remaining businesses |
What is the Process of Issuing E-Invoicing in Malaysia?
Here’s a step-by-step guide to start issuing e-invoicing in Malaysia:
1
Understand What You Need to Do
- Invoices: Details of goods/services sold, including payment amount.
- Credit Notes: Reduce amount owed (returns, overbilling).
- Debit Notes: Increase amount owed (extra charges, underbilling).
- Refund Notes: Money returned to customer.
- Consolidated Monthly Bills: Summary for retail B2C sales.
2
Choose How to Send E-Invoices
- A) Use the MyInvois Portal: MyInvois Portal is a simple website for submitting invoices. Unique code + QR code provided immediately.
- B) Use API Integration: With a MyInvois API, you can connect your ERP/billing software to MyInvois for automatic submission and validation.
3
Set Up Access & Roles
- Create or confirm your MyTax account.
- Sign up for MyInvois.
- Assign roles for invoice creation and approval.
If using API: obtain a digital certificate and set up webhooks for validation messages from IRBM.
4
Prepare Your List of Key Details
- Suppliers: Name, address, TIN, contact.
- Customers:
- B2B: Same as suppliers (TIN mandatory).
- B2C: Only if requested; otherwise, use consolidated invoice.
- Products/Services: Description, price, tax rate, SKU code.
- Invoice links: If correcting an invoice, note the original invoice reference.
5
Follow the Easy Step-by-Step Workflow
- Create the invoice (via portal or system).
- Submit it to IRBM.
- Receive a unique ID + QR code from IRBM.
- Share the validated invoice with your buyer.
Important: If the buyer requests a “cancel” within 72 hours, you’ll need to reissue the invoice. After 72 hours, use credit/debit notes.
Special Case: Retail or B2C Sales
For retail/B2C sales, you can skip issuing individual invoices if the customer doesn’t request it. However, don’t forget to submit a consolidated e-invoice monthly within 7 days after the month ends.
Issuing an E-Invoice in Malaysia: Extra Scenarios You Should Know
Importing goods or services: If you’re importing goods or services, you need to issue a self-billed e-Invoice because the seller abroad can’t use your system. Remember to submit it soon after clearing customs.
Selling internationally: You still send an e-Invoice, and the IRBM logs it. However, your foreign buyer doesn’t need to use MyInvois.
Project-based work (like construction): In cases of project-based work, you’ll need to reference the contract or job number and issue adjustments (credit/debit notes) if required. This is done especially after 72 hours.
E-Invoicing for Complex Industries
Recognising the complexity of transactions in different sectors, the government of Malaysia has also published FAQs catering to different industries.
You can access it here.
Common Mistakes While E-Invoicing & How to Avoid Them
Finally, here are some common mistakes that many business owners generally make while registering for the e-invoicing:
| Mistake | Fix |
|---|---|
| Forgetting the buyer’s TIN in B2B | Add a TIN field in your customer setup |
| Waiting too long to cancel mistakes | Set a 48-hour internal reminder to act fast |
| Missing the monthly consolidated invoice | Automate it or set a calendar alert |
| Forgetting self-billed invoices for imports | Add a step in your import process checklist |
FAQs on E-Invoicing in Malaysia
Is e-invoicing mandatory in Malaysia?
Yes, e-invoicing is mandatory in Malaysia. While the implementation is being conducted in phases, all businesses must expect to use e-invoicing by 2026.
Do you only need to create e-invoices for transactions inside Malaysia?
No, e-invoices aren’t limited to transactions within Malaysia. It is mandated for cross-border transactions as well, and the system supports foreign currencies.
Is there a grace period for implementing e-invoicing in Malaysia?
Yes, there is a grace period. The E-Invoicing Relaxation Period is granted to each group of taxpayers for six months from the official implementation date for their income bracket.
What will happen if I can’t comply with e-invoicing in Malaysia?
If you fail to issue e-invoices within six months of the grace period for your business, it may result in a fine ranging from RM200 to RM20,000 or imprisonment for up to six months. In some cases, both penalties may apply.
You can contact Malaysiabrands for assistance regarding any information presented in this article. At the same time, you can go through our list of accounting services in Malaysia if you need professional help with e-invoicing.